Ascitic taping, also known as paracentesis, is a medical procedure that involves the draining of accumulated fluid in the abdomen (ascites). This can be done for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes. Diagnostic reasons include analyzing fluids to establish causes of ascites and therapeutically reducing symptoms caused by water retention. It is typically safe and effective when carried out by experienced healthcare professionals, thereby improving patient care and comfort.
PURPOSE
01.
Diagnostic: To get a sample of the ascitic fluid for analysis leading to a diagnosis, which may include liver disease (cirrhosis), cancer, heart failure, infection or other causes.
02.
Therapeutic: This treatment relieves complaints such as stomach pain, bloating, and difficulty breathing due to the high volumes of fluid in the belly.

INDICATIONS
-
Unexplained ascites: The cause of the collection is unknown.
-
Symptomatic Ascities: Alleviate discomfort and improve quality of life.
-
Suspected infection: Diagnose spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP).
-
Malignant Ascites: Manage fluid accumulation in patients with cancer.
-
Liver Diseases: Evaluate and manage ascites in patients with cirrhosis.
PROCEDURE
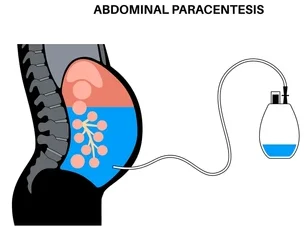
- Usually, the patient lies flat on their back or slightly turned aside when doing this procedure.
- A sterile antiseptic solution is used to clean the abdomen while local anesthetic is injected at the insertion site to numb it.
- Ultrasound guidance helps identify fluid pockets and avoids organ damage while inserting needles into body cavities.
- A sterile needle or catheter is carefully inserted through the skin & muscle into the abdominal cavity.
- When the needle reaches the correct position, fluid will be aspirated using a syringe or drained into a collection container, if any, like cysts, for example.
- Fluid collection for laboratory analysis, including cytology, culture, cell counts and protein levels.
- A therapeutic procedure may lead to the withdrawal of a greater volume of fluid in order to control symptoms.
- After the desired amount of fluid is taken out, the needle or catheter is pulled out.
- Sterile dressing covers the puncture site.
- Patients are observed briefly for complications.
Monitoring
Have to monitor patients for signs such as infection or bleeding that indicates the complications post-operatively.
POST-PROCEDURE CARE
Fluid Analysis
This is followed by further medical treatment and management based on the results obtained from examining fluids.
Follow-Up
Additional treatments or monitoring might be necessary depending on what causes ascites in an individual patient's case.
WHY TO CHOOSE US ?
Centric
